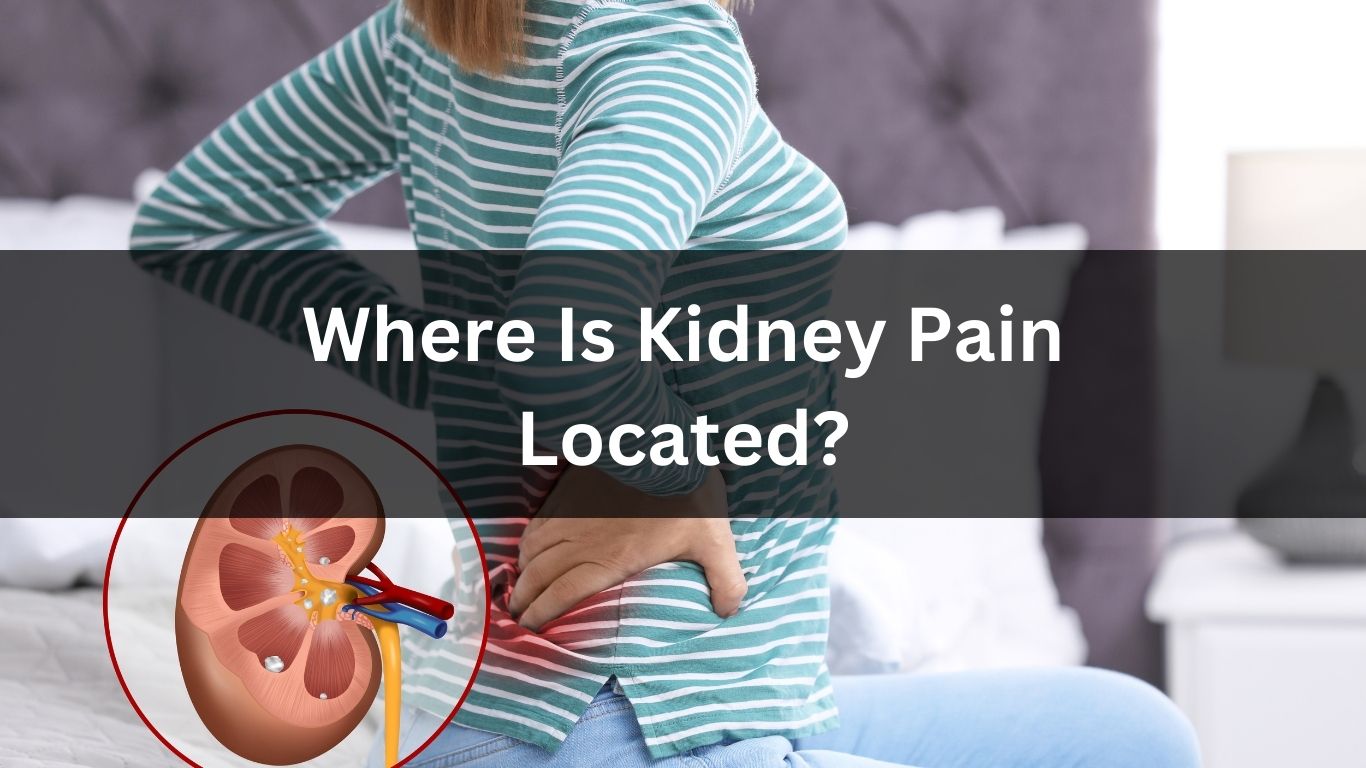
Kidney pain can be caused by various conditions, such as kidney stones, urinary tract infections, kidney infections, or kidney diseases. If you are experiencing persistent or severe kidney pain, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper treatment.
Typically, kidney pain is located in the lower back, usually on one side of the body. This pain is commonly felt in the flank area, between the lower ribs and the hips.
Early detection and prompt medical intervention can help prevent complications and promote kidney health. So, I have mentioned here some of the symptoms of kidney pain–
Key Locations And Descriptions
Kidney pain typically occurs in the lower back, just below the ribs, on either side of the spine. It can also radiate to other areas, such as the abdomen or groin.
1. Typical Areas For Kidney Pain
Kidney pain is commonly felt in the flank region, which is located on either side of the lower back, below the ribs. This region corresponds to the location of the kidneys in the body. The pain may be experienced on one side or both sides, depending on the underlying cause.
In some cases, the pain can extend to the abdomen, groin, or even the thighs. This radiation of pain is a distinguishing characteristic of kidney pain and can help differentiate it from other types of discomfort.
2. Differentiating Pain In Kidneys From Muscle Ache
It can be challenging to distinguish between kidney pain and muscle ache, especially since both can manifest as discomfort in the lower back. However, there are a few key differences that can help in differentiation. Kidney pain tends to be more severe and persistent than muscle ache.
It may also be accompanied by other symptoms, such as fever, urinary changes, or blood in the urine. On the other hand, muscle ache is often caused by physical strain or injury and may improve with rest and gentle stretching.
3. Pain Characteristics That Indicate Kidney Involvement
Several pain characteristics can indicate kidney involvement. Firstly, kidney pain tends to be deep and dull, rather than sharp or stabbing. It may also fluctuate in intensity, with periods of increased pain followed by moments of relief.
Other indicators of kidney involvement include pain that worsens with movement, such as bending or twisting, and pain that is alleviated by changing positions, such as sitting or lying down.
Additionally, accompanying symptoms like frequent urination, cloudy urine, or a persistent urge to urinate can further suggest kidney involvement.
Silent Symptoms To Watch For
Kidney pain can be silent and often goes unnoticed, but it is typically located in the back, just below the ribs. Being aware of these silent symptoms can help detect kidney problems early on.
Non-pain Related Kidney Issue Symptoms
Kidney issues can often manifest through silent symptoms that may easily go unnoticed. This is why understanding these subtle signs is crucial for early detection and prompt medical intervention.
By being aware of the non-pain related symptoms associated with kidney problems, you can take proactive steps towards maintaining your kidney health.
Changes In Urination As Symptoms
One of the key indicators of potential kidney problems is changes in your urination pattern. These changes can include:
- Urinating more frequently: If you find yourself making more trips to the bathroom than usual, it might be worthwhile to investigate further. Frequent urination can be a sign of kidney impairment.
- Urinating less frequently: On the other hand, if you notice a decrease in the frequency of urination, particularly accompanied by dark-colored urine, it could be a sign of kidney trouble.
- Presence of blood in urine: Hematuria, or the presence of blood in urine, can be an alarming indication of kidney issues. If you notice pink, red, or brown-colored urine, it’s essential to seek medical attention.
Additional Silent Symptoms That Could Signal Kidney Problems
In addition to changes in urination, there are other silent symptoms that could potentially signal kidney problems:
- Swelling: Edema or swelling in the legs, ankles, feet, or face could be a result of impaired kidney function. Pay attention to any unexplained swelling and consult a physician if necessary.
- Fatigue and weakness: Feeling excessively tired and weak, even after getting enough rest, can be associated with kidney issues. If you often experience unexplained fatigue, it’s worth considering a kidney check-up.
- Loss of appetite and weight: Kidney problems can cause a loss of appetite, leading to unintentional weight loss. If you find yourself eating less without any specific reason, it’s important to investigate the underlying cause.
- Difficulty concentrating: Impaired kidney function can result in a decrease in cognitive abilities, leading to difficulty in focusing and concentration. If you notice persistent mental fog, it’s advisable to explore potential kidney-related factors.
Clues For Pinpointing Kidney Discomfort
In order to properly diagnose kidney pain and seek appropriate medical attention, it’s essential to understand the clues that can help pinpoint kidney discomfort. Let’s delve into these clues for a better understanding of kidney pain.
Role Of Pain Location In Kidney Health Diagnosis
Unlike other types of back pain, kidney pain is not usually limited to one specific area. Instead, it tends to radiate or spread to different regions of the body. The kidneys are located on either side of the spine, tucked just below the ribcage. Therefore, kidney pain is often felt in the back, specifically in the flank area.
It’s important to note that the exact location of kidney pain can vary from person to person. Some individuals may feel the discomfort more towards the middle or lower back, while others may experience it more towards the sides.
Additionally, kidney pain can also manifest as abdominal pain, further adding to the challenge of accurate diagnosis.
Interpreting Pain Intensity And Duration
The intensity and duration of kidney pain can provide valuable insights into the severity and underlying cause. Kidney pain is often described as dull and achy, but it can also escalate to sharp and intense pain.
The pain may come and go or persist for extended periods, depending on the specific issue affecting the kidneys. Additionally, some individuals may experience intermittent bouts of pain, while others may have constant discomfort.
It’s crucial to pay attention to changes in pain intensity and duration, as sudden and severe pain could indicate a more urgent medical condition. Moreover, chronic or recurring kidney pain shouldn’t be ignored, as it may point towards an underlying chronic kidney problem that requires treatment.
When To Suspect Kidney Pain Vs. Other Types Of Back Pain?
Differentiating kidney pain from other types of back pain can be challenging, but there are certain factors to consider. If the pain radiates from the flank area, below the ribcage, and extends towards the back or abdomen, kidney pain is a probable cause. However, it’s essential to rule out other potential causes, such as muscle strains, spinal issues, or gastrointestinal problems.
Additional symptoms that may accompany kidney pain include frequent urination, bloody or cloudy urine, fever, and nausea. If you experience any of these accompanying symptoms, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation.
Kidney Pain Vs. Other Organ Pain
Kidney pain, located in the lower back or side, differs from pain in other organs. Understanding the distinct location and symptoms of kidney pain can help in identifying potential kidney issues.
Distinguishing Kidney Pain From Gallbladder Or Liver Issues
Kidney pain, in particular, may share similarities with other organ-related discomfort such as gallbladder or liver issues. However, there are certain distinguishing factors that can help differentiate kidney pain from pain originating in these organs.
- Kidney pain is typically felt in the lower back or on the sides of the abdomen.
- Pain caused by gallbladder issues, on the other hand, tends to manifest as a sharp pain in the upper right side of the abdomen.
- Liver problems often present as a dull ache or discomfort in the upper right side of the abdomen as well, but sometimes the pain can radiate to the back or shoulder as well.
Unique Nature Of Referred Pain
Referred pain is a phenomenon where pain felt from one area of the body is actually originating from a different location. The kidneys, being an essential part of the urinary system, can sometimes cause referred pain that is felt outside of their immediate vicinity. This can further complicate the accurate identification of kidney pain.
- Kidney pain may be referred to the lower abdomen or groin region, giving the impression that it is originating from the bladder.
- Similarly, kidney pain may radiate to the upper thigh, mimicking pain from the hip joint.
Comparative Analysis: Kidney Pain And Lower Back Issues
Kidney pain is often mistaken for lower back pain due to the close proximity and similar areas affected. However, distinguishing between kidney pain and lower back issues is essential for tailored treatment approaches.
- Kidney pain is typically focused on one side of the lower back, whereas general lower back pain can affect both sides.
- Kidney pain may also be accompanied by other symptoms such as frequent urination or changes in urine color and consistency.
- Lower back issues, such as muscle strains or herniated discs, may result in radiating pain down the legs.
Subtle Signs Of Kidney Issues
Kidney pain, commonly located in the back or the side of the abdomen, can often be a subtle sign of kidney issues. Recognizing these subtle signs is crucial for early detection and timely treatment.
Uncommon Symptoms That Might Point To Kidney Problems
There are several lesser-known symptoms that could indicate potential kidney problems. These symptoms may not always be directly related to the kidney itself but can provide valuable clues about underlying kidney issues.
1. Changes in urination patterns: Pay attention to any changes in the frequency, color, or odor of your urine. Increased or decreased urination, blood in the urine (hematuria), foamy urine, or strong-smelling urine can all be signs of kidney problems.
2. Fatigue and weakness: Kidney issues can lead to a buildup of waste products in the body, causing fatigue and weakness. If you find yourself constantly feeling tired even with sufficient rest, it could be a sign of kidney trouble.
3. Swelling: Kidneys play a crucial role in removing excess fluid from the body. When they are not functioning properly, fluid can accumulate, leading to swelling in the hands, feet, or ankles. Noticeable swelling, particularly in the lower extremities, should not be ignored.
Importance Of Early Detection And Symptom Recognition
Early detection of kidney issues is vital for prompt treatment and management. Recognizing the subtle signs and symptoms can help identify problems before they worsen, potentially avoiding complications and additional health issues.
When kidney problems are left untreated or undiagnosed, they can progress to more severe conditions such as chronic kidney disease or even kidney failure. The earlier the problem is identified, the better chance there is of implementing appropriate measures to protect kidney health.
Silent Symptoms In Various Demographics And What They Signify
Kidney issues can manifest differently in various demographic groups. It’s essential to be aware of these silent symptoms and what they may signify in specific populations.
| Demographic Group | Silent Symptoms | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Elderly Individuals | Confusion, decreased appetite, decreased mental sharpness | Could indicate acute kidney injury or chronic kidney disease |
| Diabetic Patients | Uncontrolled high blood pressure, recurrent urinary tract infections | May point to diabetic nephropathy, a kidney condition caused by diabetes |
| Women | Increased frequency of urinary tract infections | Might suggest a kidney infection or kidney stones |
| Children | Bedwetting, loss of appetite, frequent thirst | Could be signs of kidney stones or a urinary tract infection |

Credit: hartfordhospital.org
Conclusion
Understanding the location of kidney pain is crucial for identifying potential kidney problems. By being aware of the specific areas where kidney pain is commonly experienced, you can seek early medical attention and prevent further complications. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are key in maintaining kidney health and well-being. Stay informed and take care of your kidneys to ensure a healthy and balanced life.
FAQs Of Where Is Kidney Pain Located
How Do You Know If Pain Is From Kidney?
Pain from the kidney typically presents as a sharp or dull ache in the lower back or side area. Other signs include frequent urination, blood in urine, and fever. It’s important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
What Are The 3 Early Warning Signs Of Kidney Disease?
The three early warning signs of kidney disease include frequent urination, blood and/or foam in urine, and swelling in the legs, ankles, feet, or face.
What Are The First Signs Of Kidney Problems?
Early signs of kidney problems include frequent urination, fatigue, swelling in the legs, feet or ankles, difficulty concentrating, decreased appetite, and back or side pain. These symptoms may indicate kidney disease, so it’s important to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.
What Can Be Mistaken For Kidney Pain?
Kidney pain can be mistaken for other conditions, including muscle strains, urinary tract infections, or even appendicitis.

Nazmul Gazi is a dedicated final-year student at Cumilla Medical College with a passion for promoting health and wellness. Drawing from his medical studies, Nazmul writes insightful health tips and guides, helping readers make informed decisions about their well-being.